Checking the nutrition label is a good way to make healthier food choices. This fact sheet aims to help you understand and use the nutrition information presented on the food label.
Nutrition labels can help you choose between products and track the amount of foods you're eating that are high in fat, salt and added sugars. The Eatwell Guide also helps you choose healthy foods.

Nutrition information will appear on the food label, alongside other information including:
- Name of the food
- Weight of the food
- Ingredients, listed in order of quantity used
- Nutrition information
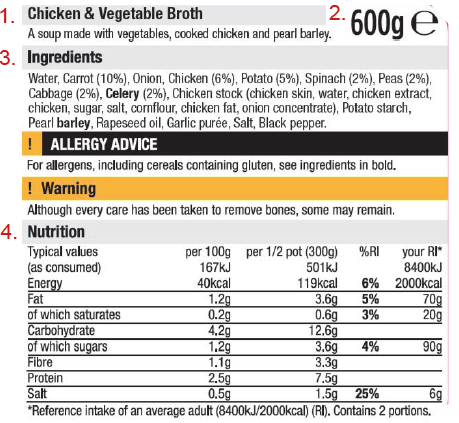
Nutrition information is legally required on all packaging larger than 10cm², with exemptions for some food items. This information is usually shown on the back or side of the product’s packaging as a table and may also appear on the front of the package (e.g. as traffic lights).
Common allergens will be shown on the ingredients list in bold. For more information about food allergen labelling, read our fact sheet on Food Allergy and Food Intolerance.
Front of pack nutrition labels
These labels show some nutrients that are important to keep an eye on for health, to help you make a quick choice. It is not currently a legal requirement for products to display this label.
If shown, the label will contain the amount of energy in calories (kcal) or kilojoules (KJ), per serving and per 100g. It will also display the amount of fat, saturates (saturated fat), sugars and salt in a serving. These are the nutrients to keep an eye on for a healthy diet.
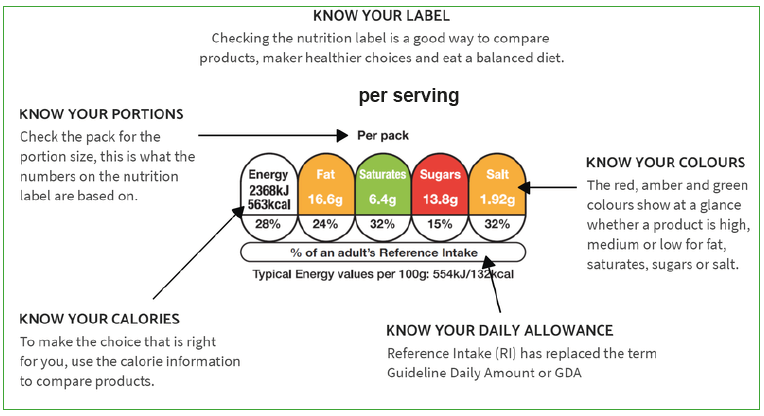
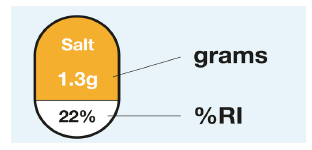
The numbers on the label show you how many calories and how much fat, saturates (saturated fat), sugars and salt a ‘serving’ of the food or drink contains. This information appears as the number of grams (g) and as a share (%) of your ‘Reference intake’ (RI) or daily allowance.
The Reference intake (RI) on a front of pack label is based on the requirements for an average woman. The average woman needs 2,000 calories per day, the average man 2,500 calories and children fewer than 2,000 calories, depending on their age.
How to use the front of pack nutrition label
For a healthier choice choose products with more greens and fewer reds. If a nutrient appears in red on the label, try to limit the number of times you eat this food. Amber means neither high nor low, so you can eat foods with all or mostly amber on the label most of the time as long as you keep under the daily allowance.
Comparing products in this way can help you select healthier choices. Use the percentages on the nutrition label to track whether you’re under or over your Reference Intake (RI) or daily allowance.
Some front of pack labels are not colour coded, so you will need to look at the percentage of RI in a portion to compare foods or drink.
Nutrition information on the back or side of the pack
Nutrition information on the back or side of a food packet is a legal requirement. As shown below, the highlighted elements must be included on all packaging:
- Nutrients per 100 grams
- Nutrients per serving (sometimes called a portion)
- Number of servings per pack
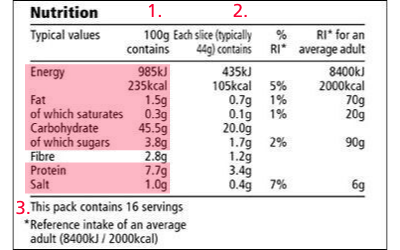
You may also see information about unsaturated fats, fibre, and vitamins and minerals – this is not legally required. But if a claim is made about a specific nutrient, for example claiming the food is a ‘source of calcium’, the amount of that nutrient (i.e. calcium) in the product must be given on the nutrition label.
How to use the back of pack nutrition label
- Use the nutrition information per 100g to make comparisons between foods
- Labels may refer to a recommended serving size that is different to the one you eat. A 'serving' may refer to one biscuit, but if you are eating two you will need to double it
- Use the percentages on the nutrition label to track whether you’re under or over your Reference intake (RI) or daily allowance
Nutrition and health claims
Two types of claims can appear on labels.
- Nutrition claims such as ‘low fat’ or ‘high fibre’
- Health claims such as ‘Vitamin D is needed for normal bone health’
Both types of claim may only be made when the product meets specific conditions for use, given in food labelling legislation. This ensures that any claim made on a label can be proven, is clear and not misleading for consumers.
Any claim will only refer to one nutrient or aspect of the product so it is important to read the nutrition label and ingredients list to get a picture of what is also provided by that product.
Products produced abroad
The information in this fact sheet refers to UK food labelling legislation. Products produced abroad but sold in the UK should have the mandatory information added, but be aware that they may not. If you buy food or drink items online or from some smaller stalls, for instance, they may not contain this information.
Top tips
- Food labels, including health claims, are subject to legal requirements to ensure the information is clear and proven
- Labels on the front of packaging are not legally required but they may appear as ‘traffic lights’ to help you make healthier choices
- Labels will show you nutritional information per 100g and per serving. Using the information per 100g will allow you to easily compare the nutrition in different products
- Remember to check how many servings the information refers to when calculating your own intake
Source(s)
Eatwell Guide: https://www.nhs.uk/live-well/eat-well/the-eatwell-guide/ and https://www.gov.uk/government/publications/the-eatwell-guide (Accessed 16/03/2022)
Gov.uk (2014) Food labelling and packaging [online] Available at: www.gov.uk/food-labelling-and-packaging/food-labelling-what-you-must-show (Accessed 16/03/2022)
NHS Choices Food Labels: https://www.nhs.uk/Livewell/Goodfood/Pages/food-labelling.aspx (Accessed 16/03/2022)
Institute of Grocery Distributors (IGD) Healthy Eating and Nutrition Information on Pack. Consumer Research and Message testing. Accessed May 2018. Available here: https://www.igd.com/charitable-impact/healthy-eating/nutrition-information-on-pack
Health and Nutrition Claims: https://www.gov.uk/government/publications/nutrition-legislation-information-sources (accessed 16/03/2022)
European Commission (2007) EC Regulation no 1924/2006 on nutrition and health claims made on foods. Available here: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/en/ALL/?uri=CELEX%3A32006R1924 (accessed 16/03/2022)
Department for Environment, Food & Rural Affairs (2014) Food standards: labelling, durability and composition [online] Available at: www.gov.uk/food-standards-labelling-durability-and-composition (Accessed 16/03/2022)
Information on allergen labelling: Food Standards Agency (nd) Labelling guidance [online] Available at: www.food.gov.uk/business-industry/guidancenotes/labelregsguidance/ (Accessed 16/03/2022)







